M270 Waste Management: An Innovative Solution for Managing Harmful Waste
M270 Waste Management: An Innovative Solution for Managing Harmful Waste
Blog Article
Your Overview to PFAS Therapy Technologies and Advantages
The frequency of PFAS contamination in water sources requires a comprehensive understanding of readily available therapy modern technologies. Each modern technology not just targets details PFAS compounds but likewise plays an essential function in improving overall water quality and protecting ecological honesty.
Recognizing PFAS Contamination
Comprehending PFAS contamination is crucial for resolving its pervasive effect on ecological and human health and wellness (m270 pfas treatment). Per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds (PFAS) are a team of synthetic chemicals widely utilized in numerous industrial and customer items as a result of their water- and grease-resistant properties. Typically located in firefighting foams, non-stick kitchenware, and water-repellent fabrics, PFAS have gone into the environment via manufacturing procedures, wastewater discharges, and leaching from garbage dumps
Once released, these substances continue in the environment, causing prevalent contamination of dirt and water sources. Their distinct chemical framework, defined by solid carbon-fluorine bonds, provides them resistant to deterioration, resulting in a sensation recognized as "permanently chemicals." As a result, PFAS can accumulate in the body and the food chain, possibly triggering negative health effects, consisting of immune system disturbance, developing issues, and an increased danger of specific cancers cells.
Regulative agencies and health companies are significantly identifying the relevance of PFAS contamination, motivating efforts to monitor, evaluate, and minimize its results. Recognizing the paths of PFAS contamination is vital for informing public policy and establishing reliable methods to protect both environmental and human wellness.
Review of Treatment Technologies
Numerous therapy technologies have been developed to resolve the obstacles postured by PFAS contamination in water and dirt. These modern technologies can be broadly classified into numerous classifications, each with its unique devices and efficiency in eliminating PFAS substances.
One noticeable approach is ion exchange, which makes use of resin products to catch and get rid of PFAS from polluted water. One more innovation, progressed oxidation processes (AOPs), utilizes solid oxidants and ultraviolet light to damage down PFAS into less hazardous compounds.

Triggered Carbon Filtering
Turned on carbon filtration is a commonly used approach for the elimination of PFAS from polluted water, recognized for its capacity to adsorb a wide variety of organic compounds. This technology uses activated carbon, a very permeable material with a substantial surface, which promotes the binding of PFAS molecules via physical adsorption. The performance of turned on carbon in removing PFAS is affected by numerous variables, including the sort of carbon utilized, the contact time, and the focus of PFAS in the water.
Among the advantages of activated carbon filtering is its convenience; it can be executed in various arrangements, such as granular triggered carbon (GAC) systems or powdered triggered carbon (SPECIAL-INTEREST GROUP) systems. GAC systems are generally employed in larger-scale applications, while special-interest group can be made use of in smaller or short-term setups. The technology is reasonably very easy to run and preserve, making it accessible for numerous water treatment facilities.
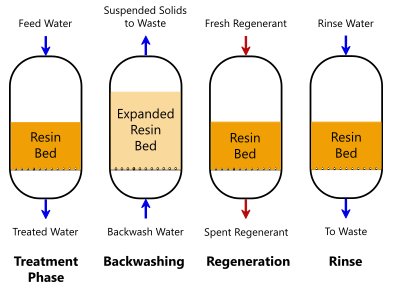
Ion Exchange Systems
Ion exchange systems stand for an additional effective approach for the removal of PFAS from polluted water, matching techniques like turned on carbon filtration. These systems operate on the concept of exchanging ions in the water with ions hung on a resin material. Ion exchange resins can be especially formulated to target the adversely charged PFAS substances, effectively catching them and permitting cleaner water to pass through.
One of the key benefits of ion exchange systems is their ability to remove a large range of PFAS, including both long-chain and short-chain versions. This adaptability makes them appropriate for different applications, ranging from metropolitan water treatment to commercial procedures. Additionally, ion exchange systems can frequently achieve reduced detection restrictions for PFAS contrasted to a few other treatment methods, therefore enhancing water top quality.
Nonetheless, it is important to keep track of and manage the regeneration of ion exchange media, as the efficiency can decline in time because of saturation. Correct upkeep and replacement of the material are navigate to this site critical for sustaining the system's efficiency. In general, ion exchange systems supply a dependable and effective solution for PFAS elimination, adding substantially to secure alcohol consumption water criteria and ecological protection.
Advanced Oxidation Processes
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) utilize effective oxidants to successfully break down PFAS substances in polluted water. These ingenious treatment methods generate very responsive types, such as hydroxyl radicals, that can damage down complicated PFAS molecules into much less dangerous by-products. m270 pfas treatment. AOPs commonly utilize mixes of ultraviolet (UV) light, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, or Fenton's reagent, improving the oxidation potential and enhancing degradation effectiveness
The key advantage of AOPs hinges on their ability to target a broad variety of PFAS compounds, including both long-chain and short-chain versions. This convenience is vital, as PFAS contamination usually entails mixes of various compounds with differing chemical frameworks. In addition, AOPs can be integrated into existing water therapy systems, making them a functional Related Site service for many districts and sectors.
Nonetheless, the implementation of AOPs can be resource-intensive, calling for mindful consideration of functional prices and energy consumption. Additionally, while AOPs are reliable in breaking down PFAS, they may not completely get rid of all by-products, necessitating more treatment actions - m270 pfas treatment. On the whole, AOPs represent an encouraging method for dealing with PFAS contamination, adding to cleaner water resources and boosted public health and wellness defense

Verdict
To conclude, attending to PFAS contamination requires a detailed understanding of readily available therapy technologies. Turned on carbon filtration, ion exchange systems, and progressed oxidation procedures each existing one-of-a-kind benefits for effectively getting rid of these hazardous substances from water sources. By choosing the ideal innovation, neighborhoods can boost water quality, protect public health, and reduce the environmental threats related to PFAS exposure. Continued research study and execution of these approaches are essential for effective administration of PFAS contamination in affected locations.
Report this page